Which Best Describes Storage Array-based Remote Replication
This chapter provides details about various local replication technologies along with restore and restart considerations. Which factor influences the write response time in a synchronous remote replication solution.
Using Storage Based Data Replication Sun Cluster System Administration Guide For Solaris Os
Which best describes Recovery Time Objective RTO.

. VMs can be protected with Hyper-V Replication or HP 3PAR Remote Copy array-based. Set up server-to-server replication. You can for example use the EMC Symmetrix Remote Data Facility SRDF or Veritas Storage Foundation for Windows for this kind of deployment.
Data can be transmitted from the source storage system to the target system over a shared or a dedicated network. SRA device management service. Install and configure Windows Admin Center on your PC.
Question 1 In pointer - based virtual replication target requires the size of the source volumes. Depending on the software you use you can use either automatic or manual failover with storage-based data replication. Changing server settings in SraConfigurationDataxml.
Effects of 10-minute synchronization interval. Best Practices When Using. The HPE MSA Storage Array and its Remote Snap feature an affordable dual storage-array with point-in-time data protection and data replication provides a disaster-tolerant solution.
Support for four Remote Replication groups. Array performing replication operations is called control array. The architecture can be scale-up or scale-out and host interface protocols can be block-based file-based or a combination of.
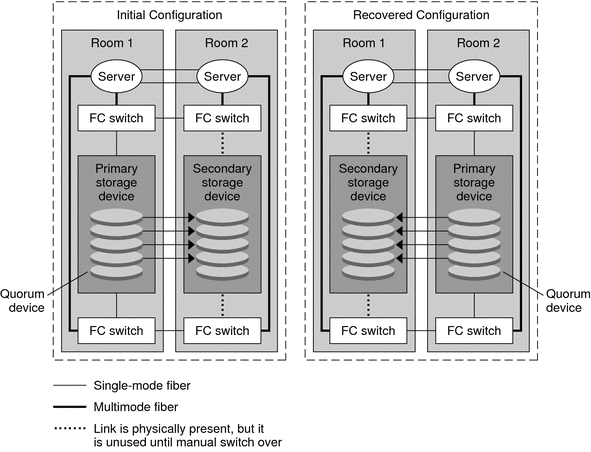
Figure 4-1 shows a sample two-room configuration where data is replicated between two storage arrays. June 22 2017 Share on. This ensures that in the event of a disaster there is zero data loss.
The array-based Remote Snap replication feature implemented with two HPE MSA storage system solutions provides a business site with ultimate data protection. Up to 5 cash back Storage ArrayBased Local Replication Copy on First Access CoFA Copy on First Write CoFW Restore and Restart Replication is the process of creating an exact copy of data. This allows you to.
Having a remote disaster recovery DR site protects against system and site-wide outages. Data is pulled to the control array from remote array. Push Data is pushed from control array to remote array Pull.
One of the key decisions when implementing SRM is which technology to use and for what VMs. Array-based replication Array-based replication for business continuity can incorporate the creation of local copies of data within the same array as the source data as well as the creation of. Provision operating system features roles storage and network.
7 SRM supports two different replication technologies Storage Array or Array-Based Replication and vSphere Replication. In this case SteelHeads optimize connections that are initiated directly between the SAN arrays participating in the replication. This chapter also details local replication in a virtualized environment.
Many SAN arrays support replication using direct connectivity via TCPIP. Array-based replication tools such as EMCs SRDF Symmetrix Remote Data Facility and NetApps SnapMirror do have their advantages however. Distance between source and remote site.
What is characteristic of. Our customers can get seamless end-to-end storage array-based replication and disaster recovery that is optimized to deliver the. But it is limited to homogeneous storage environments as it requires similar source and target arrays.
Because vSphere Replication is independent of the underlying storage it works with a variety of storage types including VMware vSAN vSphere Virtual Volumes traditional SAN network-attached storage NAS and direct-attached storage DAS. Question 5 Which accurately describes the role of a backup server. Replication is a software feature that synchronizes data to a remote system within the same site or a different location.
Synchronous replication is a data protection solution which ensures each block of data written to a storage resource is first saved locally and to a remote image before the write is acknowledged to the host. Gathers the data that is to be backed up and send it to storage node Manages the backup operation and maintains backup catalog Responsible for writing the data which client sends. Array-based replication is more resilient and requires little cross-departmental coordination when deployed.
The two technologies can be used together in an SRM environment though not to protect the same VM. In storage system-based remote replication the replication is performed between storage systems. Synchronous replication writes data to the primary and secondary sites at the same time.
Remote replication is the process of copying production data to a device at a remote location for data protection or disaster recovery purposes. Replacing DFS Replication with Storage Replica. Explore Azure load balancing services and find the best solution for your workloads using an easy-to-use service selection tool.
Adding an Azure VM connected to your network via ExpressRoute. This section describes storage-based data replication as used in a campus cluster. This section describes storage-based data replication as used in a campus cluster.
Array-based replication allows compatible storage arrays to use built-in software to automatically copy data between arrays. Specialized replication technique that enables creating remote point in time copies used for data mobility migration and disaster recovery moves data between heterogenous storage arrays. Replicating data helps to provide data redundancy and safeguards against storage system failures at the main production site.
Data replication was usually implemented using the functions of a high-end storage array in a SAN. Creating one or more replicas of the production data is one of the ways to provide Business Continuity BC. With asynchronous replication there is a delay.
Up to 5 cash back Local replication refers to replicating data within the same array or the same data center. Remote replication may be either synchronous or asynchronous. Typically one of the storage systems is in source site and the other system is in remote site for DR purpose.
Remote replication refers to replicating data at a remote site. Primary storage arrays can be utilized for mission-critical workloads including IBM Db2 Microsoft SQL Microsoft Exchange and SharePoint Oracle Databases SAP HANA and in-house-developed transactional applications. The following table shows a best practice configuration running RiOS 553 or later with TCPIP connectivity directly from storage array.
In this configuration the primary storage array is contained in the first room where it provides data to the nodes in both rooms. Sun Cluster supports both manual and automatic failover of the replicants with Hitachi TrueCopy and EMC Symmetrix Remote Data Facility software. Changing virtual memory in NesSvcini.
In synchronous replication solutions there are also trade-offs.

No comments for "Which Best Describes Storage Array-based Remote Replication"
Post a Comment